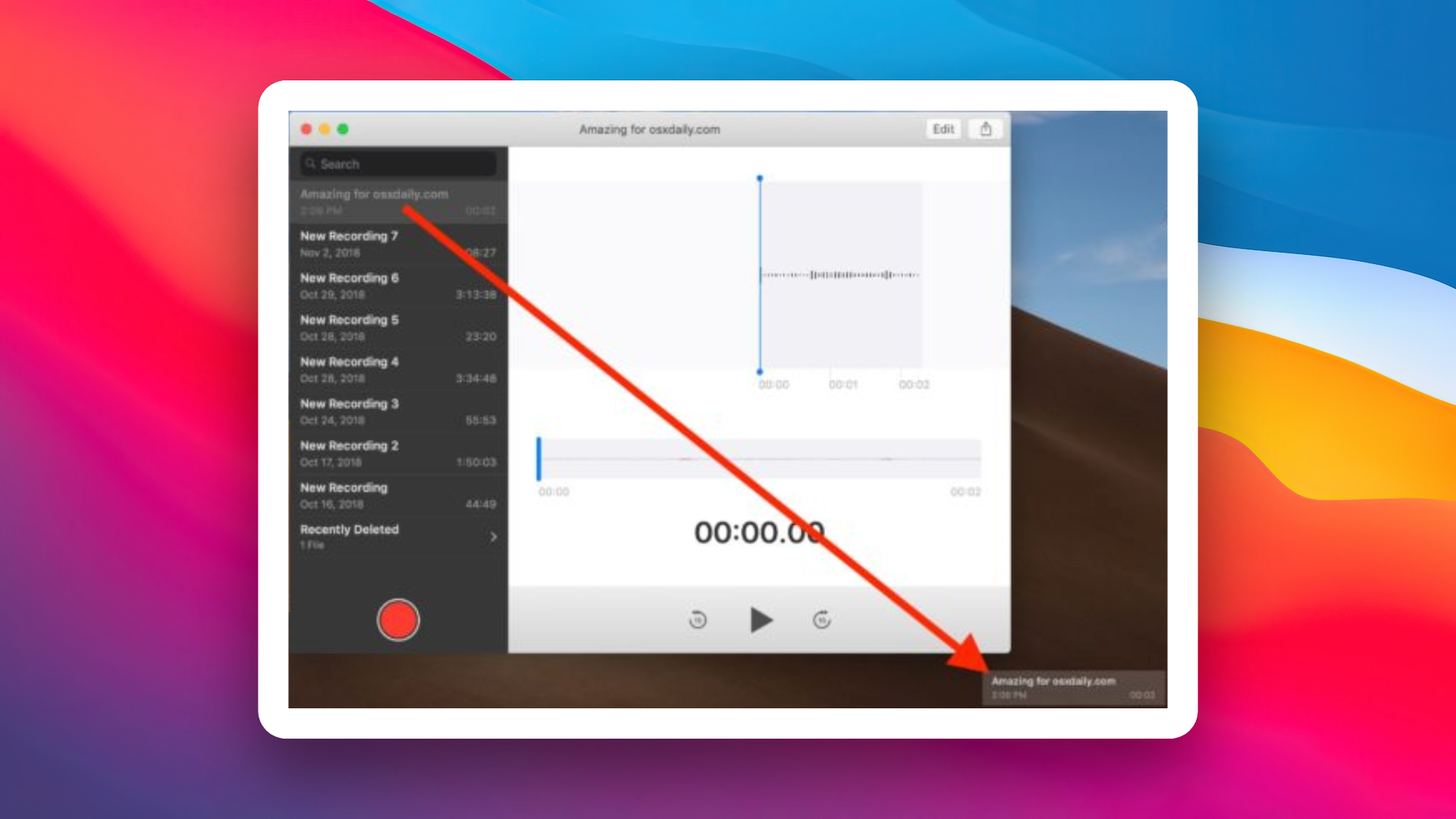
How to Save Voice Memos on the Mac as Audio Files
If you’ve recorded precious voice memos on your Mac device and want to save them as audio files, you may find that, despite the Mac’s reputation for rich file handling,...
Read More





Published on Jul 21, 2024 by taroyuyu on Computer

Intel’s Core series of processors, namely the Core i3, i5, and i7, have been the staple of computing performance for several years. Each of these processors caters to different user needs and offers varying levels of performance. In this article, we will delve into the key differences between the Core i3, i5, and i7 processors in a Markdown format.
Intel Core i3: Positioned as the entry-level processor, the Core i3 is designed for mainstream users who perform daily tasks like browsing the web, document editing, and light gaming.
Intel Core i5: Falling into the mid-range category, the Core i5 is a versatile processor suitable for moderate gaming, multimedia applications, and multitasking.
Intel Core i7: As the flagship processor, the Core i7 is aimed at high-end users who engage in demanding tasks such as professional design work, heavy gaming, and processing large amounts of data.
Core i3: Offers basic performance for everyday tasks. Intel officially positions it as a “simplified version” of the Core i5.
Core i5: Provides more robust performance than the i3, suitable for moderate gaming and multimedia applications.
Core i7: Delivers the highest performance, excelling at multitasking, heavy gaming, and professional applications.
In summary, the Intel Core i3, i5, and i7 processors differ significantly in price, performance, technical specifications, and intended use cases. Choosing the right processor depends on your individual needs and budget. The Core i3 is ideal for basic tasks, the Core i5 strikes a balance between performance and cost, while the Core i7 is the ultimate choice for demanding workloads.

If you’ve recorded precious voice memos on your Mac device and want to save them as audio files, you may find that, despite the Mac’s reputation for rich file handling,...
Read More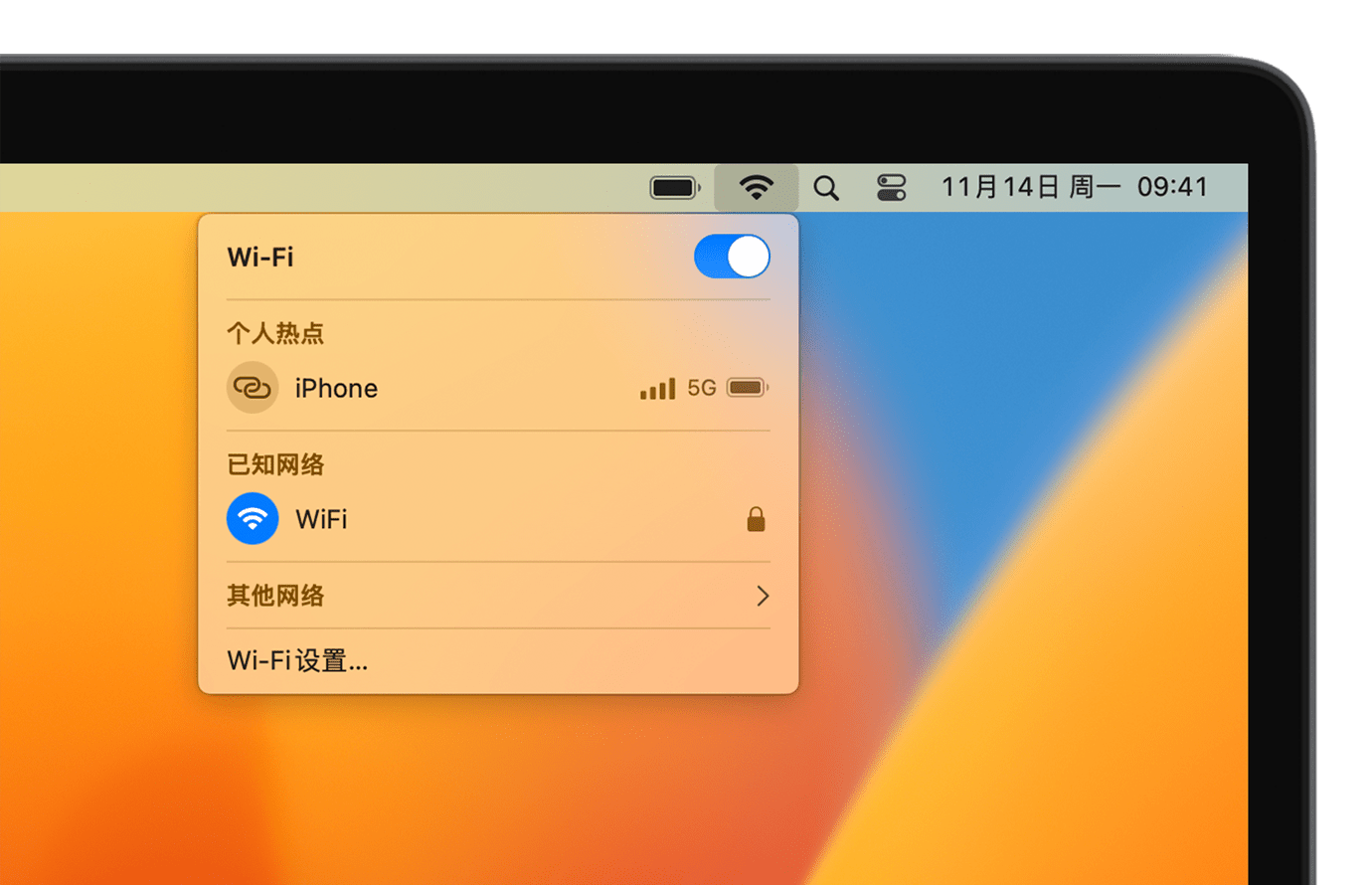
Connecting your Mac to the Internet is always within reach, no matter where you are, whether in a cozy home, a busy office, or a cafe on the go. Two...
Read More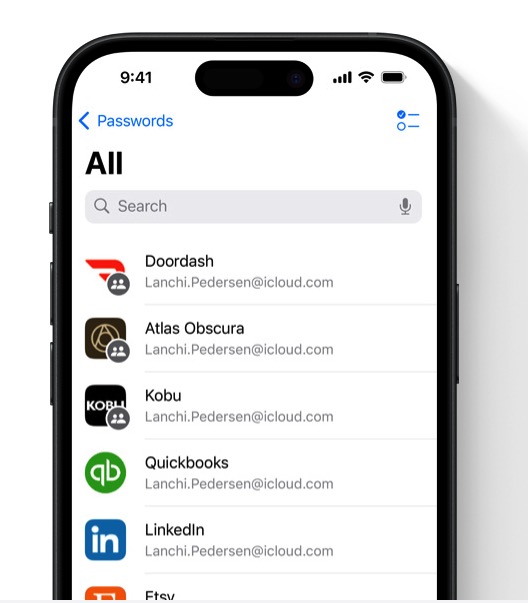
In a glittering update to iOS 18, Apple has meticulously reinvented its password management tool, the Passwords app, taking it to unprecedented heights. The core mission of the app is...
Read More